Configuring Oracle Database, Version 5.2
SL Docs
Analytics
This section describes the required configurations as well as the optional configurations available for the Solution Package for Oracle Database in the RTView Configuration Application. You must define the classpath to the Oracle JDBC jar files and you must also define data source connections for each connection that you want to monitor.
Configuring Data Collection
To configure data collection:
- Navigate to the Solution Package Configuration > Oracle Database > CONNECTIONS tab.
- On the CONNECTIONS tab, provide the correct full path to the directory containing the Oracle JDBC jar files in the Classpath field.
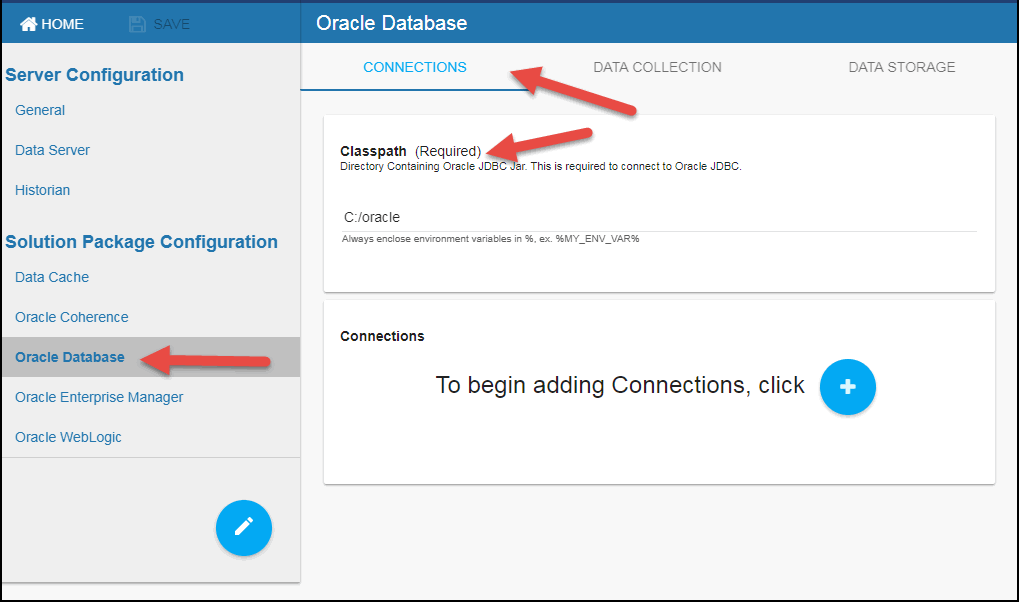
- Click the
 icon.
icon.
The Add Connection dialog displays.
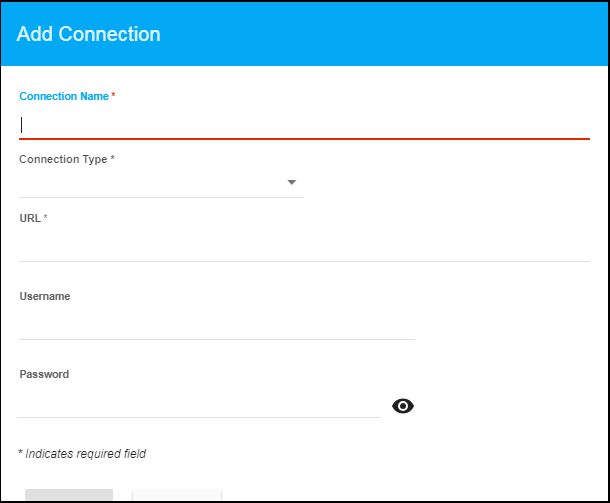
- Specify the connection information and click Save where:
Connection Name: Enter the name of the connection.
Connection Type: Select the type of connection (RAC, Standard, or XE).
URL: Specify the path to the Oracle Database to which you want to connect.
Username: The username used when connecting to the database. This field is only required when the connection has been secured.
Password: The password used when connecting to the database. This field is only required when the connection has been secured. By default, the password entered is hidden. Click the ![]() icon to view the password text.
icon to view the password text.
Once saved, the new connection displays in the Connections region on the CONNECTIONS tab.
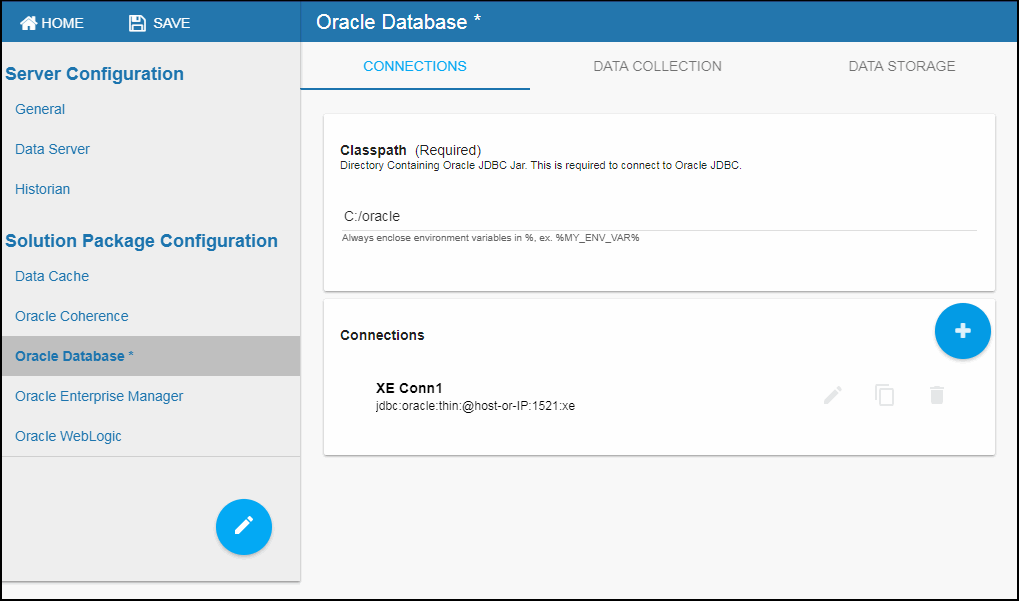
- Repeat the previous two steps for each connection to be monitored.
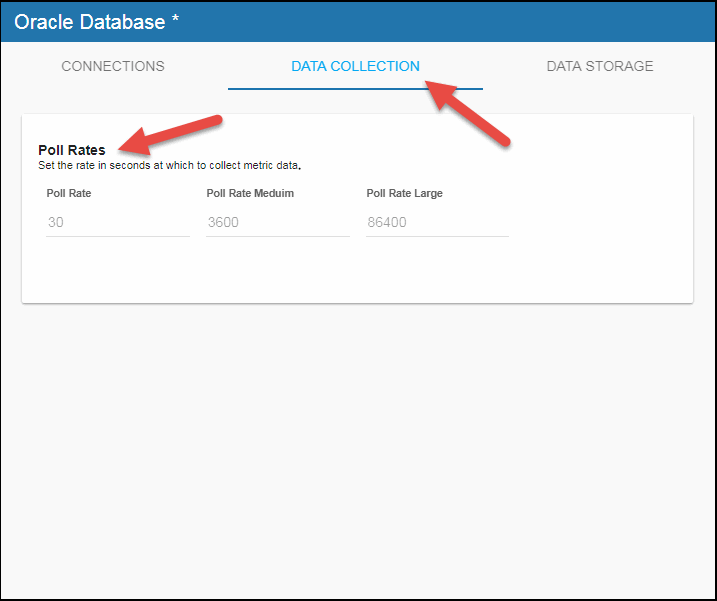
- If you want to modify the default values for the update rates for all caches, you can update the default polling rates in Solution Package Configuration > Oracle Database > DATA COLLECTION > Poll Rates. The following cache(s) are impacted by the settings in these fields:
Poll Rates: OraInstanceInfo, OraInstanceSessionStats, and OraInstanceQueryExecStats.
Poll Rates Medium: OraInstancePerformanceStats, OraInstanceHitRatio, and OraDatabaseTablespaceUsage.
Poll Rates Large: OraDatabaseDiskUsage
Note: When modifying your update rates, you should take your system architecture and number of elements per cache into account and ensure that you are not changing your update rates to values that might negatively impact system performance.
Configuring Collection of Historical Data (Optional)
You can specify the number of history rows to store in memory, the compaction rules, the duration before metrics are expired and deleted, and the different types of metrics that you want the Historian to store in the DATA STORAGE tab in the RTView Configuration Application. This section is optional.
Defining the Storage of In Memory History
You can modify the maximum number of history rows to store in memory in the DATA STORAGE tab. The History Rows property defines the maximum number of rows to store for the OraInstanceSessionStats, OraDatabaseDiskUsage, OraInstanceQueryExecStats, and OraDatabaseAvailability caches. To update the default settings:
- Navigate to the Solution Package Configuration > Oracle Database > DATA STORAGE tab.
- In the Size region, click the History Rows field and specify the desired number of rows.
Defining Compaction Rules
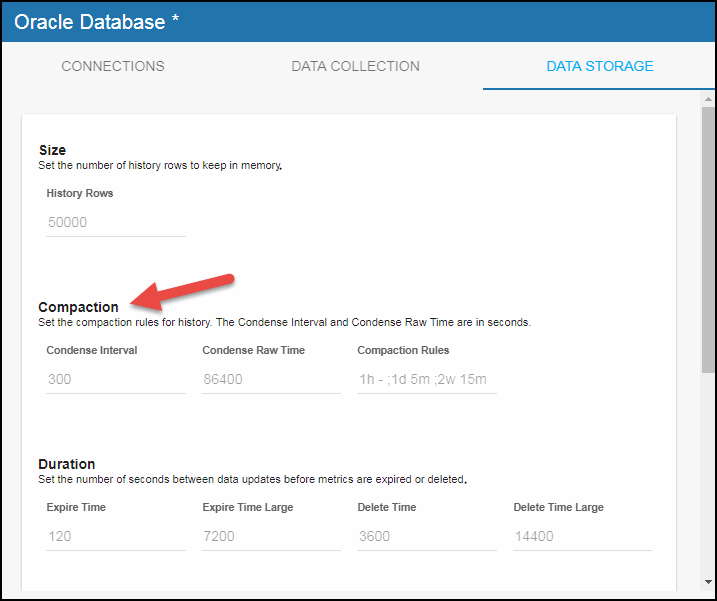
Data compaction, essentially, is taking large quantities of data and condensing it using a defined rule so that you store a reasonably sized sample of data instead of all of your data, thus preventing you from potentially overloading your database. The available fields are:
Condense Interval -- The time interval at which the cache history is condensed for the following caches: OraInstanceSessionStats, OraInstanceQueryExecStats, and OraDatabaseAvailability. The default is 300 seconds.
Condense Raw Time -- The time span of raw data kept in the cache history table for the following caches: OraInstanceSessionStats, OraInstanceQueryExecStats, and OraDatabaseAvailability. The default is 86400 seconds.
Compaction Rules -- This field defines the rules used to condense your historical data in the database for the following caches: OraInstanceSessionStats, OraInstanceQueryExecStats, and OraDatabaseAvailability. By default, the columns kept in history will be aggregated by averaging rows with the following rule 1h -;1d 5m;2w 15m, which means the data from 1 hour will not be aggregated (1h - rule), the data over a period of 1 day will be aggregated every 5 minutes (1d 5m rule), and the data over a period of 2 weeks old will be aggregated every 15 minutes (2w 15m rule).
To modify these settings:
- Navigate to the Solution Package Configuration > Oracle Database > DATA STORAGE tab.
- In the Compaction region, click the Condense Interval, Condense Raw Time, and Compaction Rules fields and specify the desired settings.
Note: When you click in the Compaction Rules field, the Copy default text to clipboard link appears, which allows you copy the default text (that appears in the field) and paste it into the field. This allows you to easily edit the string rather than creating the string from scratch.
Defining Expiration and Deletion Duration Metrics
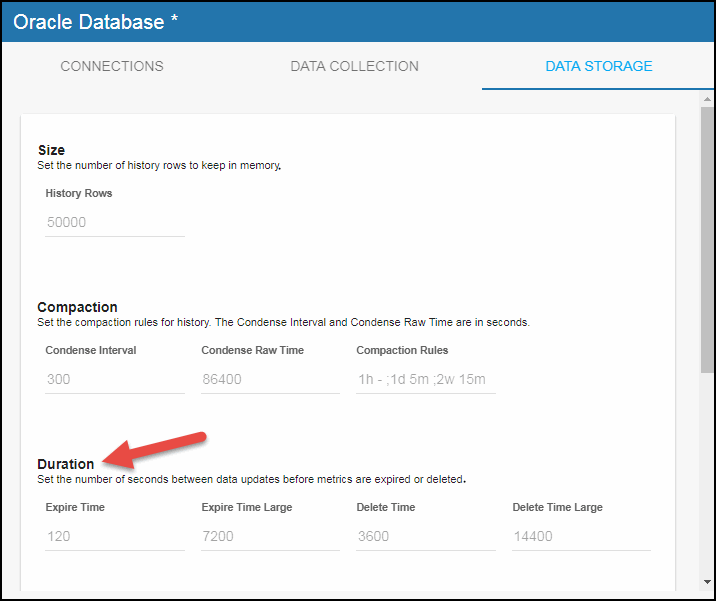
The data for each metric is stored in a specific cache and, when the data is not updated in a certain period of time, that data will either be marked as expired or, if it has not been updated for an extended period of time, it will be deleted from the cache altogether. The following lists the impacted caches and their defaults for each of the fields:
Expire Time: The number of seconds to wait for a data update before cached history data is shown as Expired in displays. The default is 120 seconds. The caches impacted by this field are OraInstanceInfo, OraInstanceSessionStats, OraInstanceQueryExecStats and OraDatabaseAvailability.
Expire Time Large: The number of seconds to wait for a data update before cached history data is shown as Expired in displays. The default is 7200 seconds. The caches impacted by this field are OraInstancePerformanceStats, OraInstanceHitRatio and OraDatabaseTablespaceUsage.
Delete Time: The number of seconds to wait for a data update before cached history data is removed from displays. The default is 3600 seconds. The caches impacted by this field are OraInstanceInfo, OraInstanceSessionStats and OraInstanceQueryExecStats.
Delete Time Large: The number of seconds to wait for a data update before cached history data is removed from displays. The default is 14400 seconds. The caches impacted by this field are OraInstancePerformanceStats, OraInstanceHitRatio and OraDatabaseTablespaceUsage.
To modify these defaults:
- Navigate to the Solution Package Configuration > Oracle Database > DATA STORAGE tab.
- In the Duration region, click the Expire Time, Expire Time Large, Delete Time, and Delete Time Large fields and specify the desired settings.
Enabling/Disabling Storage of Historical Data
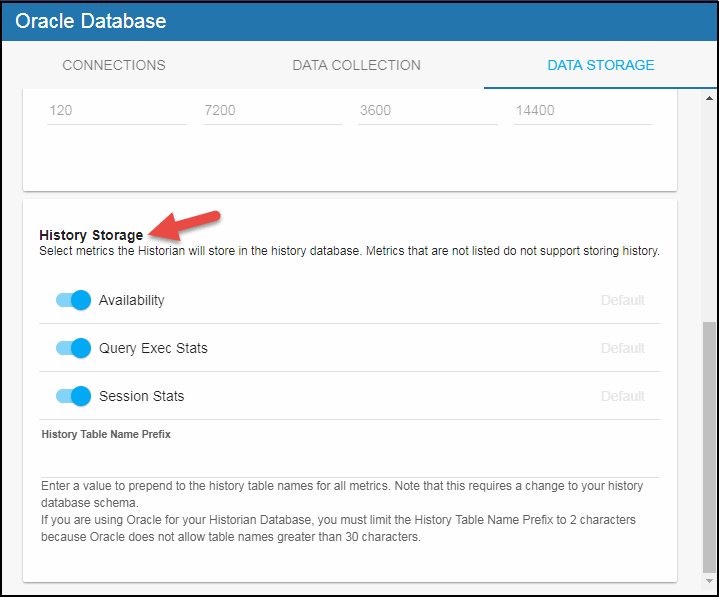
The History Storage section allows you to select which metrics you want the Historian to store in the history database. By default, the following historical data is saved to the database: Availability (OraDatabaseAvailability cache), Query Exec Stats (OraInstanceQueryExecStats cache), and Session Stats (OraInstanceSessionStats cache). The remaining historical data cannot be saved to the historian database. To enable/disable the collection of historical data, perform the following steps:
- Navigate to the Solution Package Configuration > Oracle Database > DATA STORAGE tab.
- In the History Storage region, (de)select the toggles for the various metrics that you (do not) want to collect. Blue is enabled, gray is disabled.
Defining a Prefix for All History Table Names for Metrics
The History Table Name Prefix field allows you to define a prefix that will be added to the database table names so that the Monitor can differentiate history data between data servers when you have multiple data servers with corresponding Historians using the same solution package(s) and database. In this case, each Historian needs to save to a different table, otherwise the corresponding data server will load metrics from both Historians on startup. Once you have defined the History Table Name Prefix, you will need to create the corresponding tables in your database as follows:
- Locate the .sql template for your database under rtvapm/oramon/dbconfig and make a copy of the template.
- Add the value you entered for the History Table Name Prefix to the beginning of all table names in the copied .sql template.
- Use the copied .sql template to create the tables in your database.
Note: If you are using Oracle for your Historian Database, you must limit the History Table Name Prefix to 2 characters because Oracle does not allow table names greater than 30 characters (and the longest table name for the solution package is 28 characters).
To add the prefix:
- Navigate to the Solution Package Configuration > Oracle Database > DATA STORAGE tab.
- Click on the History Table Name Prefix field and enter the desired prefix name.
